Learning Objectives
By the end of this article, you will:
- Automate advanced vSphere tasks involving NSX and Aria Operations.
- Use PowerCLI to manage NSX logical switches, firewall rules, and Aria Operations alerts.
- Integrate Python for orchestration, scheduling, and reporting of complex workflows.
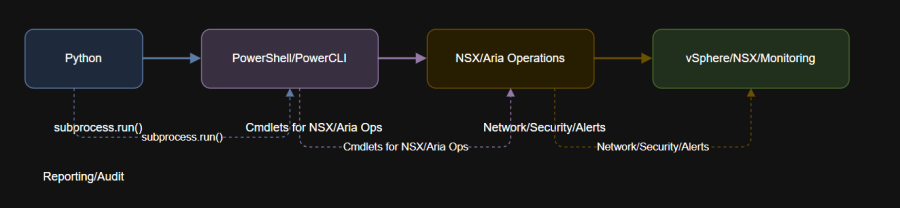
- Visualize complex automation with an diagram.
My Personal Repository on GitHub
VMware Repository on GitHub
Prerequisites
- Completed Articles 1–7.
- PowerCLI modules for NSX and Aria Operations installed (see below).
- vCenter, NSX-T Manager, and Aria Operations access with automation privileges.
1. PowerCLI and NSX-T Integration
PowerCLI supports NSX-T for advanced network automation. You can create logical switches, manage firewall rules, and more.
Importing the NSX-T Module
Import-Module VMware.VimAutomation.Nsx
Example: List All NSX Logical Switches
# Connect to NSX-T Manager
Connect-NsxtServer -Server <nsxt-manager> -User <username> -Password <password># List all logical switches
Get-NsxtLogicalSwitch | Select DisplayName, Id, TransportZoneId
Disconnect-NsxtServer -Confirm:$false
Example: Add a Firewall Rule
# Add a simple firewall rule (example)
New-NsxtFirewallRule -SectionId <section-id> -Name "Allow Web" -Action Allow -Source <src-group> -Destination <dest-group> -Service "HTTP"
2. PowerCLI and Aria Operations Integration
PowerCLI can interface with Aria Operations for monitoring, alerts, and health checks.
Example: Query Recent Alerts from Aria Operations
# Connect to Aria Operations (formerly vRealize Operations)
Connect-OMServer -Server <aria-ops-server> -User <username> -Password <password># Get active alerts
Get-OMAlert | Where-Object {$_.Status -eq "Active"} | Select Name, Resource, Severity, StartTime
Disconnect-OMServer -Confirm:$false
3. Orchestrating Advanced Automation with Python
You can automate these tasks on a schedule or trigger using Python.
Here’s a sample Python script to run an NSX-T PowerShell script and parse output for reporting.
import subprocess
import pandas as pdps_script = r"C:Automationget_nsx_switches.ps1"
completed_process = subprocess.run([
"powershell.exe",
"-ExecutionPolicy", "Bypass",
"-File", ps_script
], capture_output=True, text=True)
if completed_process.stdout:
# Parse table output to DataFrame if formatted as CSV in PowerShell
data = pd.read_csv(pd.compat.StringIO(completed_process.stdout))
print(data.head())
else:
print("No output or script failed.")
4. Diagram: Advanced Automation Integration
5. Best Practices for Advanced Automation
- Modular Scripts: Break large tasks into functions or separate scripts for easier maintenance.
- Secure Credentials: Always use encrypted credentials or secure vaults.
- Audit Trails: Log every change for compliance and rollback.
- Test in Lab: Always test automation scripts in a non-production environment first.
- Error Handling: Add robust try/catch blocks and validate outputs.
6. Troubleshooting Tips
- If you get module errors, confirm you have installed NSX-T and Aria Operations modules:
Install-Module VMware.VimAutomation.Nsxt -Scope CurrentUser Install-Module VMware.VimAutomation.VROps -Scope CurrentUser - Use full paths and explicit credentials in scripts.
- For API-related failures, validate endpoint URLs and user permissions.
7. Further Reading
8. Conclusion and Next Steps
You have now automated advanced VMware tasks that span NSX, Aria Operations, and vSphere using both PowerCLI and Python.
This approach lets you build scalable, auditable, and intelligent automation workflows across your hybrid cloud and SDDC stack.
Next up: In Article 9, you will learn to integrate PowerCLI with external APIs and tools to expand your VMware automation beyond native scripts.