In our previous article, we showed you how to install TrueNAS server. This article will guide you through configuring TrueNAS to set up ZFS storage disks and create NFS shares, enabling you to store and share data efficiently across your network.
Hardware Requirements
Before diving into the configuration of TrueNAS, ensure that you have a minimum of two disks properly connected and recognized by the system to create a ZFS pool.
However, three or more disks are recommended for better performance and redundancy (RAID-Z1, RAID-Z2, or RAID-Z3).
Configuring ZFS Storage Disks
To add a ZFS storage disk, navigate to Storage > Disks and click on the Add Disk button to select and configure the disks you want to use for storage.
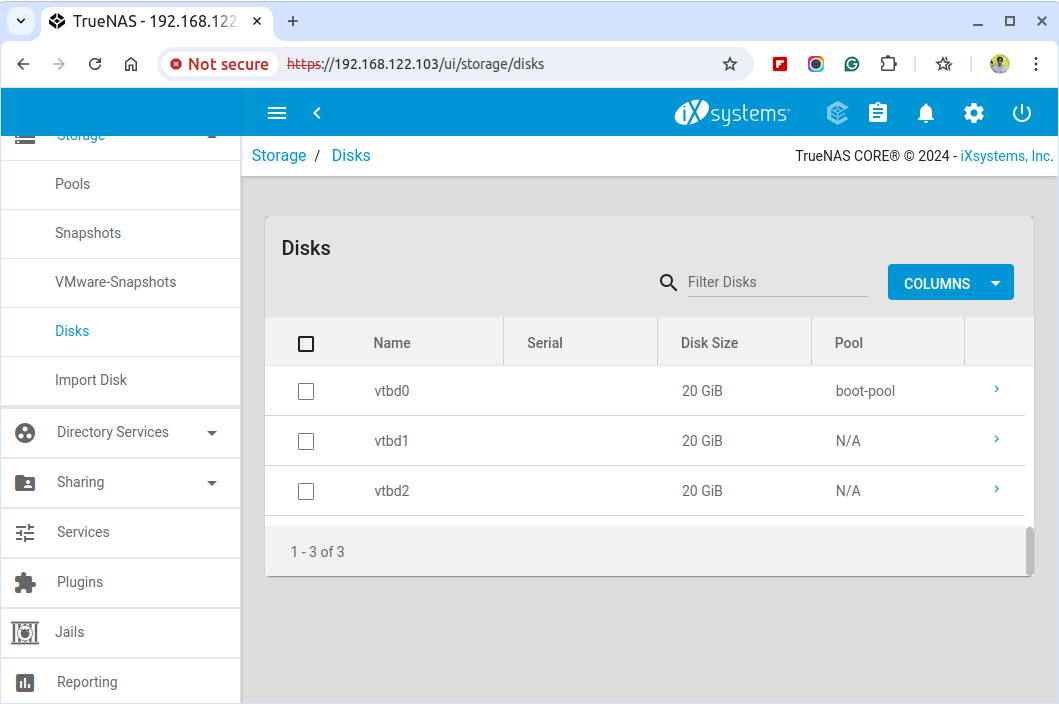
To create a ZFS Pool, navigate to Storage > Pools and click on the Add button to create a new pool.
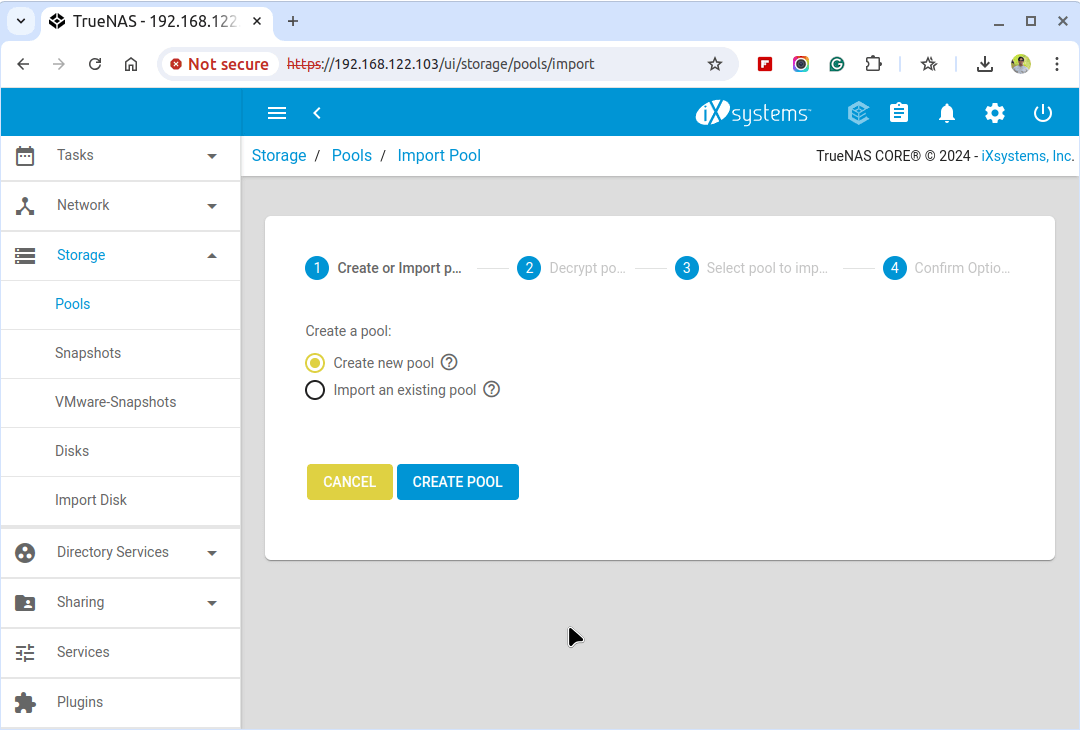
Next, enter a name for your pool and select the disks you want to include in the pool from the available list.
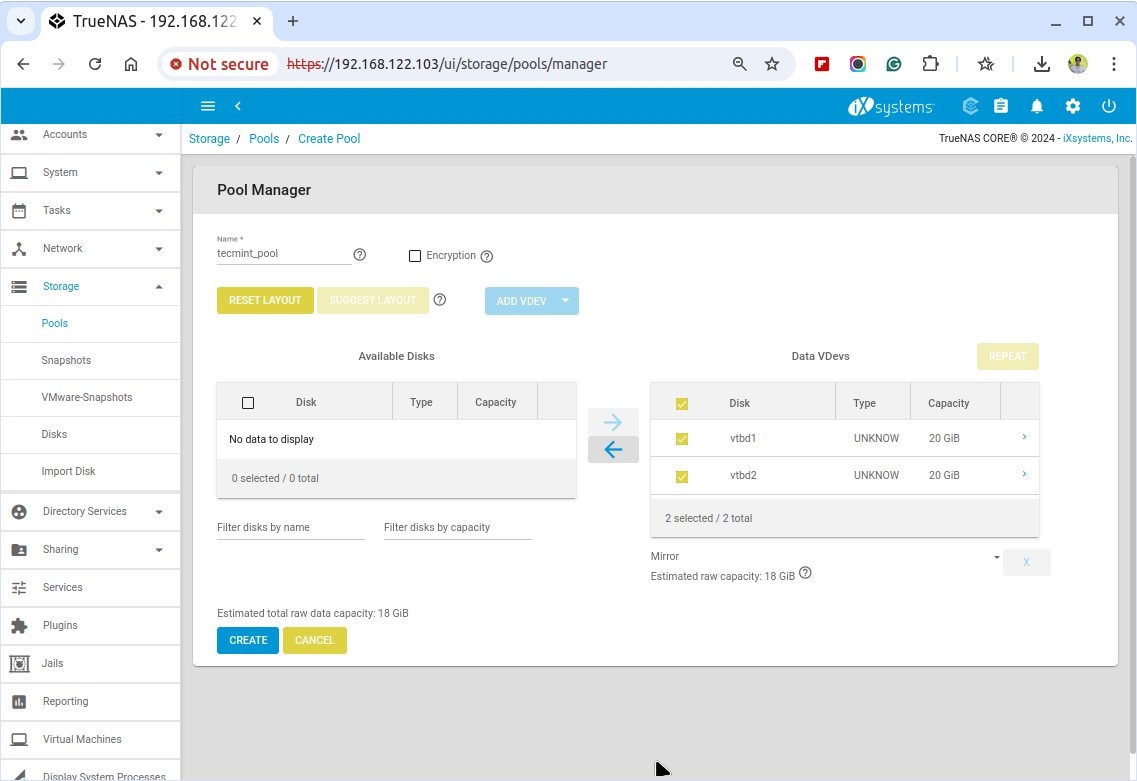
Your ZFS pool is now set up and ready for use.
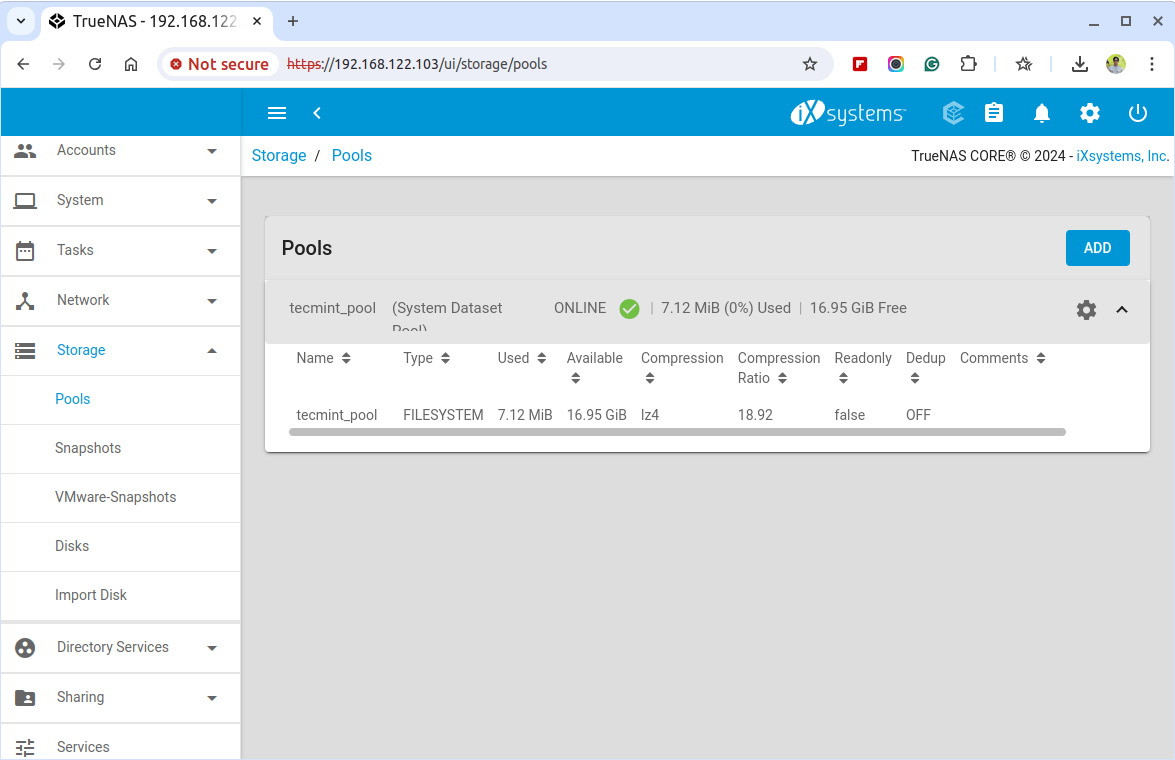
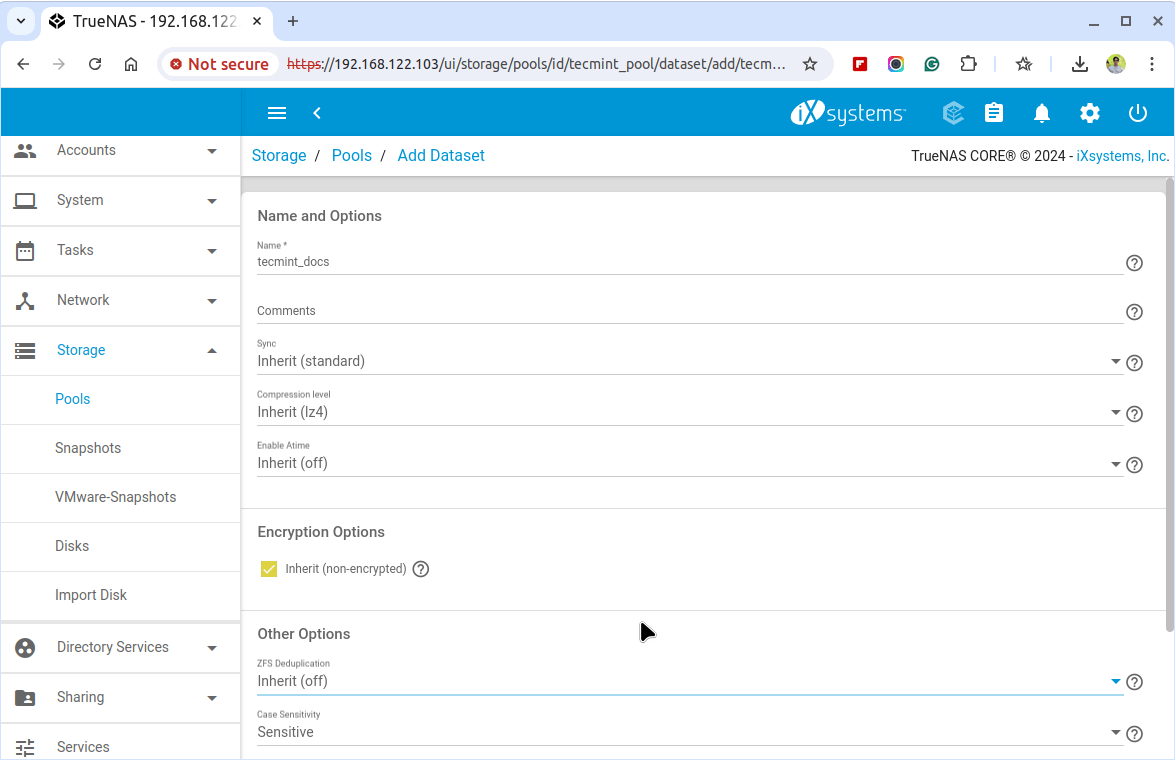
After creating the storage pool, click on the pool you just created and click on the ... (three dots) next to it and choose Add Dataset to create a new dataset.
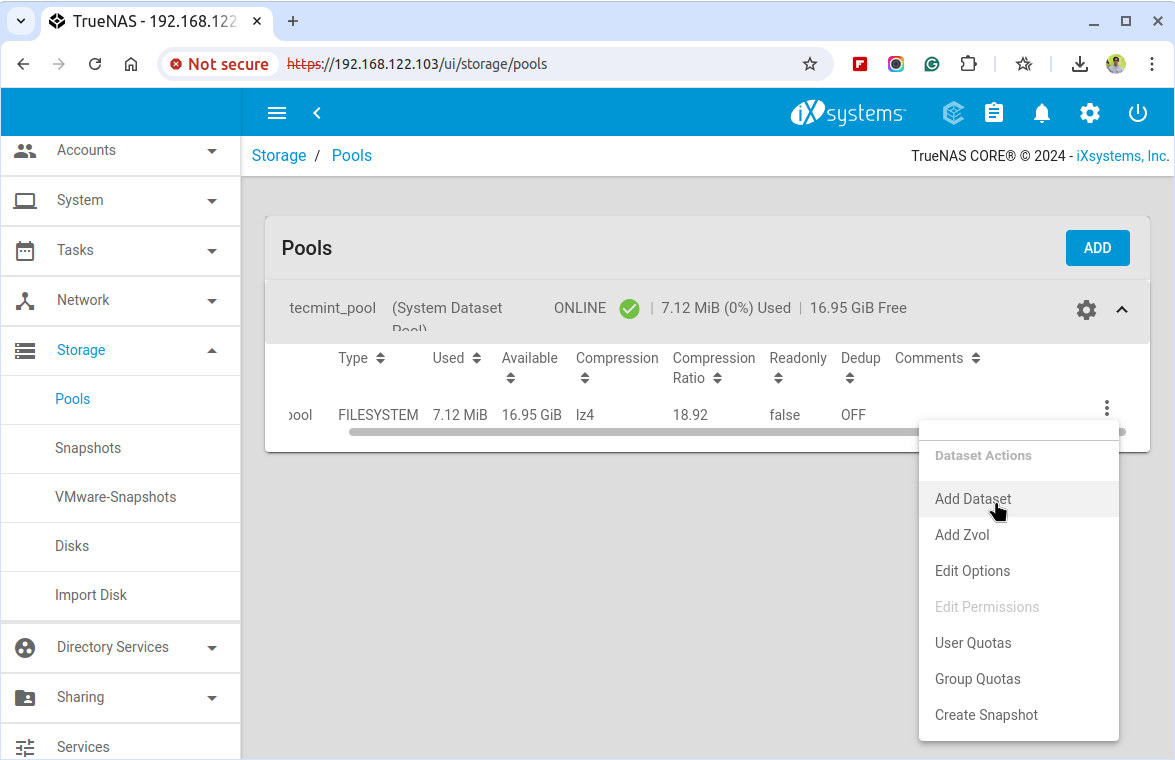
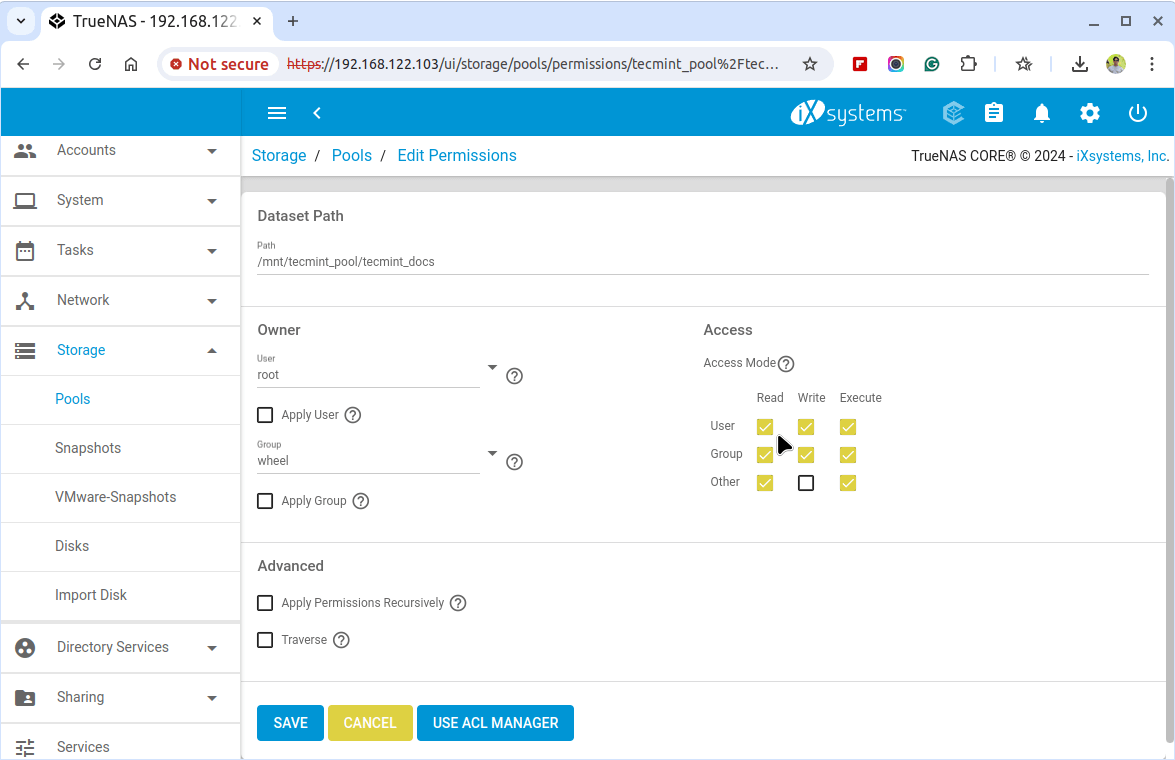
Next, enter a name for the dataset and configure the permissions for the dataset by navigating to the Permissions tab. Set the owner and group permissions, as well as read, write, and execute permissions as needed.
Creating NFS Shares for ZFS Datasets
To share ZFS datasets on Unix machines, go to the “Sharing” tab from the top menu, and choose the Unix Shares (NFS) type.
Next, click on the Add NFS Share button choose the location of the dataset you created earlier, and configure the share settings, including options for read/write access and allowed hosts.
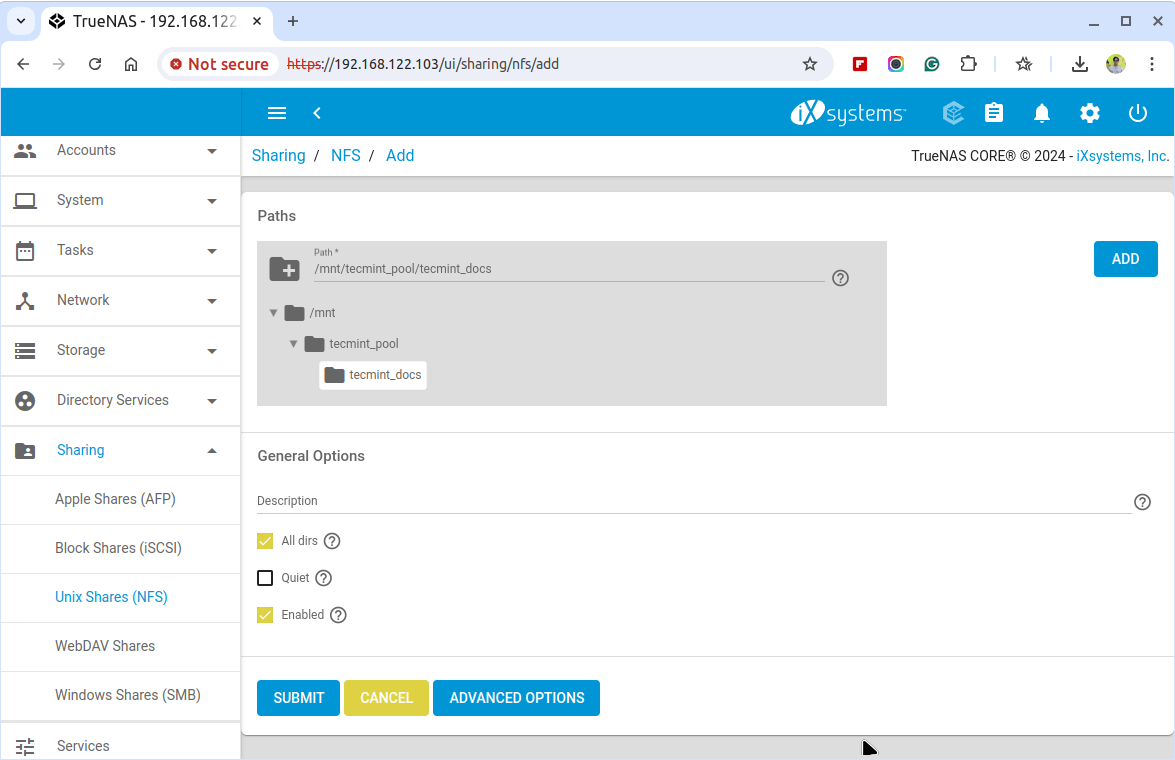
After clicking on Submit, a confirmation message will prompt, asking if you would like to enable this service. Click Yes to enable the sharing. You will then see that the NFS service has been started.
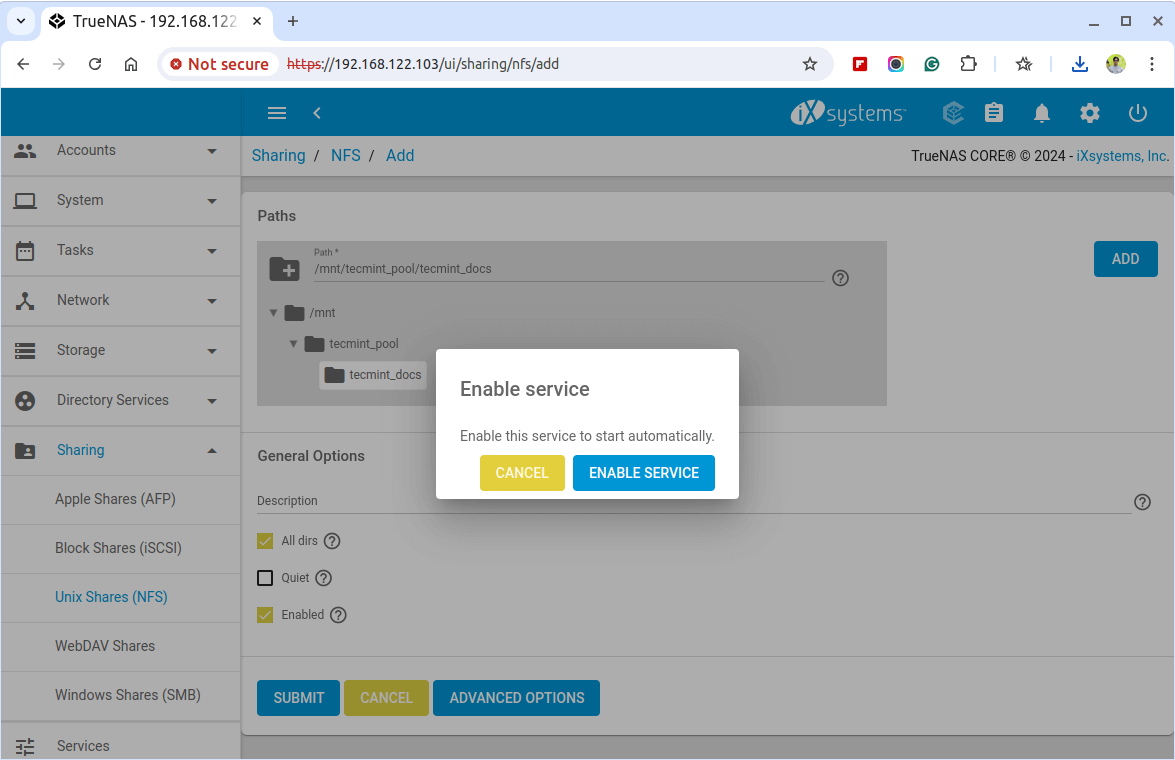
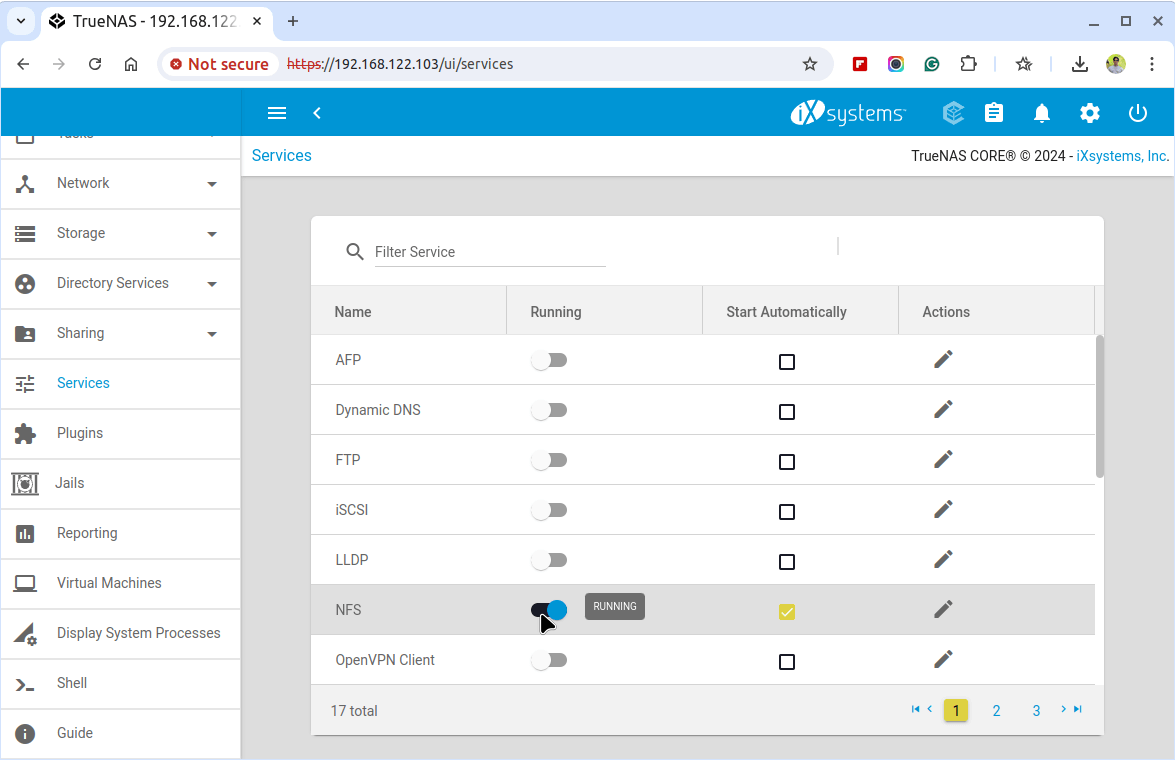
To confirm the NFS service status, navigate to Services and look for the NFS service. Make sure the toggle is in the ON position to confirm that the service is running.
Mounting NFS Share on Unix Client
Now login to your Unix client machine (Here I’ve used Ubuntu 22.04 with IP Address 192.168.122.12), and check whether NFS share from TrueNAS works or not.
But, before checking TrueNAS NFS shares, your client machine must have the NFS package installed on the system.
sudo dnf install nfs-utils -y [On RedHat systems] sudo apt install nfs-common -y [On Debian systems]
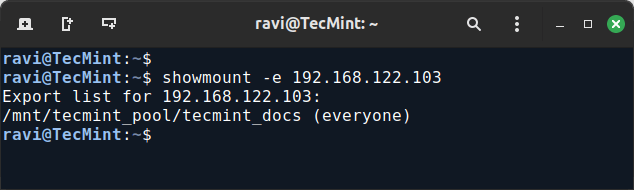
After installing NFS, use the following command to list the NFS share from TrueNAS.
showmount -e 192.168.122.103
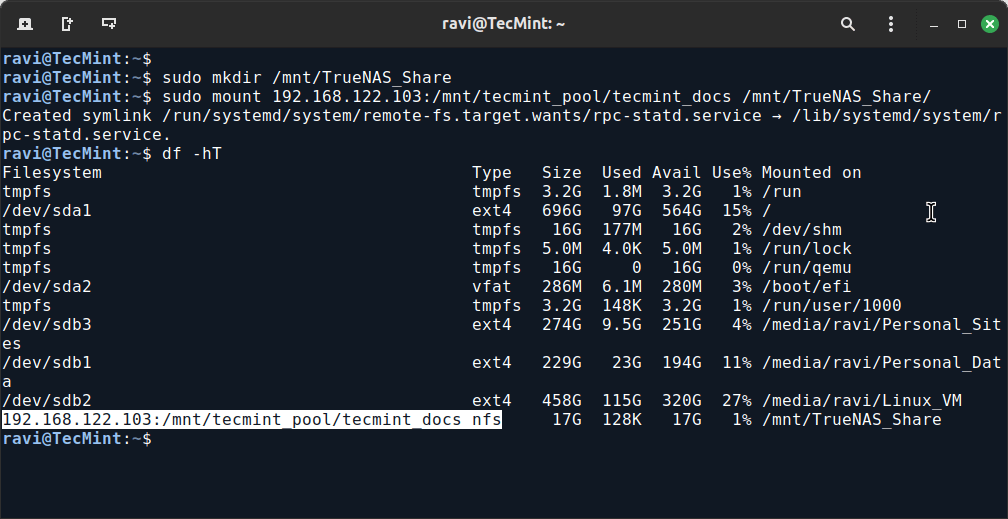
Now, create a mount directory under ‘/mnt/TrueNAS_Share‘ in the client machine, mount the TrueNAS NFS Share in this mount point, and confirm it using the df command.
sudo mkdir /mnt/TrueNAS_Share sudo mount 192.168.122.103:/mnt/tecmint_pool/tecmint_docs /mnt/TrueNAS_Share/ df -hT
Once the NFS share is mounted, go inside that directory and try to create a file under this share to confirm that the root user has permission to this share.
sudo su cd /mnt/TrueNAS_Share/ touch tecmint.txt
That’s it! we have configured the storage volume and defined an NFS share from TrueNAS.
Conclusion
TrueNAS provides a user-friendly interface to manage the storage server. TrueNAS supports a large file system using ZFS with features such as compression, quotas, and permissions.
In future articles, we’ll explore how to use TrueNAS as a streaming server and torrent server.