Systemd is a system and service manager for Linux operating systems, providing a standard process for controlling what services start when the system boots.
Sometimes, you may need to remove a systemd service for various reasons, such as it being no longer necessary, conflicting with other services, or you simply want to clean up your system.
Systemd uses unit files to manage services, which are typically located in /etc/systemd/system/ or /lib/systemd/system/. These unit files define how the service should start, stop, and behave.
Removing a systemd service involves stopping the service, disabling it so it doesn’t start on boot, and then deleting its unit file.
This guide will walk you through the steps to remove systemd services in Linux.
Identifying Systemd Service
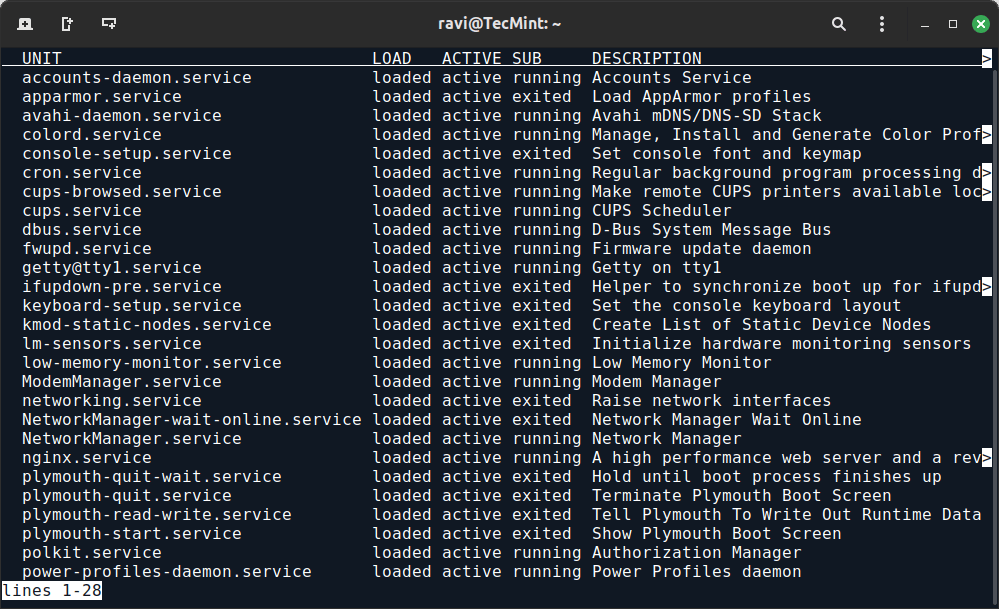
First, you need to identify the exact name of the service you wish to remove by listing all the active services using the following command.
systemctl list-units --type=service
Or, if you know the service name or a part of it, you can use.
systemctl | grep <service-name>
Stopping and Disabling Systemd Service
Before removing a service, it’s important to stop it if it is currently running by using the following systemctl command.
sudo systemctl stop <service-name>
To prevent the service from starting automatically on boot, you need to disable it.
sudo systemctl disable <service-name>
Removing Systemd Service
Finally, remove the service’s unit file from the system, which is usually located in /etc/systemd/system/ or /lib/systemd/system/ using the rm command to delete the file.
sudo rm /etc/systemd/system/<service-name>.service
Or, if it’s located in the other directory.
sudo rm /lib/systemd/system/<service-name>.service
After removing the unit file, reload the systemd configuration to reflect the changes.
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
Conclusion
Removing systemd services on Linux involves stopping the service, disabling it from starting on boot, and deleting its unit file.
Always verify that the service is no longer needed and that you have the necessary permissions to perform these actions.