Introduction
AI agents are reshaping automation by moving from simple scripts to adaptive, intelligent systems that can plan, reason, and act on real goals. Unlike traditional software, these agents can gather data, analyze information, break down objectives, and execute steps, all with a surprising degree of autonomy and flexibility. Today, you will learn how to create a robust AI agent using CrewAI, integrate it with Clarifai’s high-performance models, and leverage key design patterns for reliability and transparency.
What Sets AI Agents Apart?
AI agents are not just basic bots. They are software entities that can:
- Operate autonomously: Decide on actions without constant user input
- Perceive context: Pull live data from APIs, databases, or sensors
- Reason and plan: Break big problems into smaller, actionable tasks
- Take action: Execute code, generate content, or trigger API calls
- Learn and adapt: Evolve by incorporating feedback and new experiences
- Retain memory: Remember user preferences and past interactions
- Communicate: Work with other agents for complex, collaborative workflows
While LLMs supply the intelligence, agents add structure, connecting tools, memory, and logic for end-to-end workflows.
Agentic Design Patterns: Building Reliable Systems
Intelligent agents do more than generate responses. They use tested patterns to manage complexity:
- Reflection: Agents review their own outputs, critique mistakes, and improve on the fly.
- ReAct (Reason + Act): Combines thoughtful planning with tool execution, cycling between reasoning steps and real-world actions.
- Multi-Agent Collaboration: Distributes tasks among specialized agents (like a researcher, summarizer, or coder) for greater speed and modularity.
Often, these patterns are combined for scalable, error-tolerant automation.
Agentic System Architecture
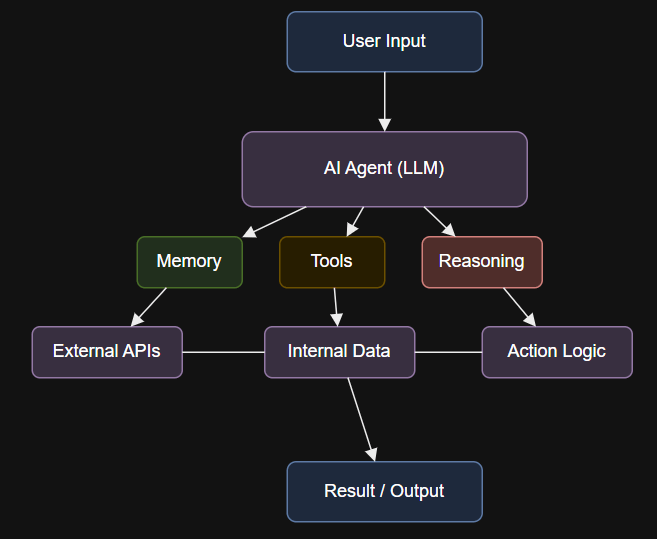
Step-by-Step: Build a Blog-Writing Agent
Let’s put theory into practice by building a single-agent workflow that researches, plans, and drafts a blog post.
1. Define Your Tools
A “tool” is a function the agent can call. For blog writing, start with a research tool:
from crewai.tools import tool@tool("Research Tool")
def fetch_research_data(query: str) -> str:
# Replace this mock with a real API or web scraping logic
return f"Research data for '{query}': Key trends, stats, and insights from top sources."
2. Configure the Language Model (Clarifai LLM)
CrewAI works with any OpenAI-compatible endpoint. Here’s how to use Clarifai’s DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B:
import os
from crewai import LLMclarifai_llm = LLM(
model="openai/deepseek-ai/deepseek-chat/models/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B",
base_url="https://api.clarifai.com/v2/ext/openai/v1",
api_key=os.environ.get("CLARIFAI_PAT")
)
3. Assemble the Agent, Task, and Crew
Define the agent’s role, capabilities, and backstory, then assign a task and create a crew:
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew, Process# Agent: The writer
blog_writer = Agent(
role="Blog Writing Specialist",
goal="Research topics and draft high-quality, structured blog posts.",
backstory="You are an expert blogger with a talent for distilling research into engaging content.",
tools=[fetch_research_data],
verbose=True,
allow_delegation=False,
llm=clarifai_llm
)
# Task: The blog writing job
blog_task = Task(
description=(
"Write a blog post on 'The Future of AI Agents'. "
"Cover recent breakthroughs, industry trends, and practical use cases."
),
expected_output="A full markdown blog draft.",
agent=blog_writer
)
# Crew: The orchestrator
project_crew = Crew(
agents=[blog_writer],
tasks=[blog_task],
process=Process.sequential,
verbose=True
)
4. Execute the Workflow
Run the agent, triggering the entire research and drafting process:
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("Launching blog-writing agent...")
result = project_crew.kickoff()
print("Blog Draft Complete!n")
print(result)
The agent uses your research tool, generates content with the Clarifai model, and produces a polished blog draft in markdown.
Key Takeaways
- Modularity: You can add more agents (like editors or SEO specialists) for larger workflows.
- Tooling: Swap or upgrade tools as your needs grow—anything callable from Python can become an agent tool.
- Flexibility: CrewAI and Clarifai together allow you to use cutting-edge models while keeping your codebase clean and maintainable.
When to Use (and When Not to Use) Agents
AI agents offer powerful automation, but not every task requires their complexity. For simple jobs, a basic LLM call or workflow may suffice. Agents are best for:
- Orchestrating multi-step processes
- Integrating with APIs, databases, or internal systems
- Handling tasks with shifting requirements or dynamic feedback
Start simple, then scale as complexity grows.
Conclusion
Building a modern AI agent is now approachable for any developer. By combining CrewAI’s orchestration tools with Clarifai’s efficient LLM endpoints, you can create agents that research, plan, and execute sophisticated tasks, bringing true intelligence and autonomy to your automation stack.