Learning Objectives
By the end of this article, you will:
- Automate common VM lifecycle actions such as power on, power off, and restart.
- Create and manage VM snapshots through scripts.
- Build reusable Python-driven PowerCLI automation for these tasks.
- Visualize the process with a step-by-step diagram.
My Personal Repository on GitHub
VMware Repository on GitHub
Prerequisites
- Completed Articles 1–3 (PowerCLI and Python are installed, and you have scripts working).
- vCenter or ESXi access with permission to modify VMs and create snapshots.
- Windows system with PowerCLI.
1. Introduction to VM Lifecycle Automation
Managing VMs at scale is much easier when you automate frequent actions like starting, stopping, restarting, and snapshotting. PowerCLI makes these tasks scriptable, while Python lets you orchestrate and schedule them as part of broader automation workflows.
2. PowerShell Script: Power On, Power Off, Restart, and Snapshot VMs
Below is a PowerShell script that demonstrates how to:
- Connect to vCenter
- Power on, power off, and restart a VM
- Take a snapshot of a VM
- Log results to a file
Save as vm_lifecycle.ps1:
# Import PowerCLI
Import-Module VMware.PowerCLI# Connect to vCenter (update details)
Connect-VIServer -Server <vcenter-address> -User <username> -Password <password>
# Set your VM name
$vmName = "<your-vm-name>"
# Power on VM
Start-VM -VM $vmName -Confirm:$false | Out-File -FilePath C:Templifecycle_log.txt -Append
# Take snapshot
New-Snapshot -VM $vmName -Name "AutoSnapshot_$(Get-Date -Format 'yyyyMMdd_HHmmss')" -Description "Automated snapshot via script" | Out-File -FilePath C:Templifecycle_log.txt -Append
# Restart VM
Restart-VMGuest -VM $vmName -Confirm:$false | Out-File -FilePath C:Templifecycle_log.txt -Append
# Power off VM
Stop-VM -VM $vmName -Confirm:$false | Out-File -FilePath C:Templifecycle_log.txt -Append
# Disconnect
Disconnect-VIServer -Server * -Confirm:$false
Replace <vcenter-address>, <username>, <password>, and <your-vm-name> as needed.
3. Calling the Lifecycle Script from Python
Here is the Python code to execute the above PowerShell script and print the output:
import subprocessps_script = r"C:Tempvm_lifecycle.ps1"
completed_process = subprocess.run([
"powershell.exe",
"-ExecutionPolicy", "Bypass",
"-File", ps_script
], capture_output=True, text=True)
print("Script Output:", completed_process.stdout)
if completed_process.stderr:
print("Errors:", completed_process.stderr)
You can schedule or trigger this script from other Python programs as needed.
4. Diagram: VM Lifecycle Automation Flow
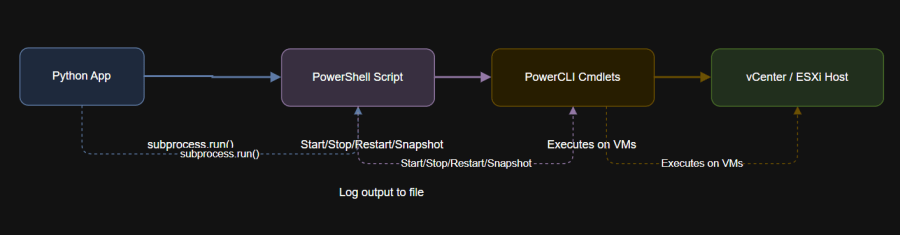
5. Best Practices and Safety Tips
- Snapshot Management:
Do not keep snapshots for long periods. Regularly remove old snapshots to avoid storage and performance issues. - Permissions:
Scripts that modify VM states should be run only by trusted admins. - Testing:
Always test scripts in a lab before using in production. - Logging:
Use log files to keep a history of automated actions for auditing and troubleshooting.
6. Further Reading
7. Conclusion and Next Steps
You have learned how to automate VM lifecycle management and snapshotting using PowerCLI and Python.
These scripts enable faster recovery, testing, and bulk management for your vSphere environment.
Next up: In Article 5, you will learn how to export and visualize your VM inventory and script outputs using Python for reporting and analytics.