Introduction
The Action Layer is the hands and voice of agentic AI, where all upstream planning, reasoning, and perception are finally translated into concrete results. This layer is responsible for executing decisions, interacting with external systems, and delivering measurable outcomes. In enterprise architectures, the Action Layer connects intelligent agents to the real world by automating business processes, sending notifications, updating records, triggering workflows, or even controlling physical devices. A resilient and well-designed Action Layer ensures that plans are enacted reliably, securely, and at scale, serving as the operational endpoint of the entire agentic stack.
What This Layer Is and Why It Matters
The Action Layer is where abstract AI intent becomes tangible impact. It transforms approved plans and decisions into API calls, database transactions, emails, chatbot responses, and machine or robotic commands. This layer must be capable of handling failures, managing transactions, ensuring data integrity, and integrating with diverse enterprise systems. The Action Layer is essential for closing the loop between intelligent analysis and business value, without it, agentic AI cannot deliver outcomes or prove return on investment. In regulated industries, the Action Layer is also critical for auditability, logging, and enforcement of security or compliance policies.
Diagram
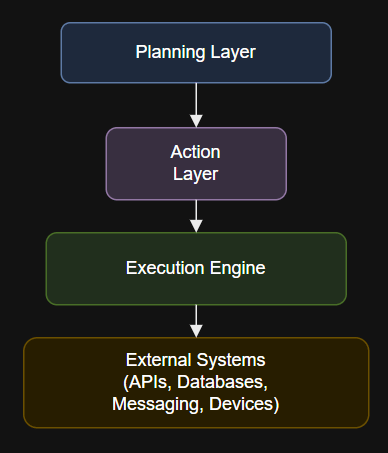
Deep Dive: Components and Data Flow
- Execution Engine: Responsible for translating plans into executable steps, managing order, and handling errors or retries.
- Adapters and Connectors: Interface with APIs, databases, messaging systems, or IoT devices, abstracting protocol and vendor differences.
- Transaction and State Management: Ensures reliable, idempotent execution with rollback and logging in case of failure.
- Audit and Compliance Hooks: Captures action logs, enforces policy, and integrates with monitoring or SIEM tools for enterprise oversight.
Integration Points
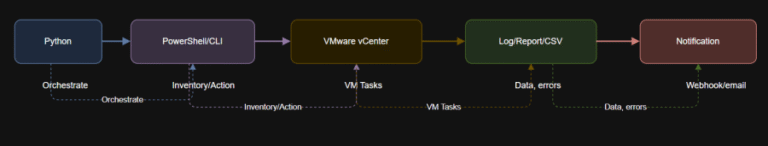
Popular enterprise tools include Apache Camel for system integration, Celery or Prefect for distributed task execution, REST or GraphQL APIs, and RPA platforms like UiPath or Automation Anywhere. Use cases cover order fulfillment, customer support automation, IT remediation, industrial robotics, and beyond.
Production Ready Script Example (Python, REST API Action Execution with Celery)
Below is a real-world Python script using Celery for executing tasks that interact with external APIs, a pattern common in enterprise automation.
Prerequisites: Python 3.9 or newer, celery, requests, a running message broker such as RabbitMQ or Redis.
from celery import Celery
import requests
import osBROKER_URL = os.getenv("CELERY_BROKER_URL", "redis://localhost:6379/0")
app = Celery("action_layer", broker=BROKER_URL)
@app.task(bind=True, max_retries=3)
def execute_api_action(self, endpoint, payload):
try:
response = requests.post(endpoint, json=payload, timeout=10)
response.raise_for_status()
return {"status": "success", "response": response.json()}
except Exception as exc:
self.retry(exc=exc, countdown=5)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Example: Execute a real-world action—create a support ticket via REST API
endpoint = "https://api.example.com/support/ticket"
payload = {
"customer_id": "CUST123",
"issue": "Server outage in region A",
"priority": "high"
}
result = execute_api_action.delay(endpoint, payload)
print("Action execution task submitted:", result.id)
This script shows robust action execution with retries, error handling, and API integration—typical for enterprise AI-driven operations.
External Reference
Learn more about distributed task execution and integration for enterprise AI:
Celery Documentation
Conclusion
The Action Layer is the ultimate enabler of business value in agentic AI. By reliably executing complex, multi-system operations, this layer ensures that all upstream intelligence results in meaningful, measurable outcomes. For enterprises, a strong Action Layer is the foundation of scalable automation, compliance, and operational excellence. Designing for reliability, traceability, and adaptability in this layer is crucial for any AI system that aims to make a real-world impact.