Learning Objectives
By the end of this article, you will:
- Implement error handling in both PowerCLI and Python scripts.
- Add log file creation for task auditing and troubleshooting.
- Integrate VMware automation scripts with Aria for Logs.
- Visualize end-to-end logging with an diagram.
My Personal Repository on GitHub
VMware Repository on GitHub
Prerequisites
- Completed Articles 1–5.
- Admin access to your vSphere environment and Aria for Logs (if using log integration).
- PowerCLI, Python, and permissions to write log files.
1. Why Error Handling and Logging Matter
Automation is powerful, but things go wrong: network issues, permissions, resource exhaustion, and more.
Good scripts should log what happened and handle errors gracefully so you know where to look when something fails.
2. PowerCLI Error Handling and Logging
Try/Catch and Log to File
Below is a PowerShell script that wraps key actions in error handling and logs both success and failure.
Save as vm_error_handling.ps1:
# Import PowerCLI
Import-Module VMware.PowerCLI# Define log file
$logFile = "C:Tempautomation_log.txt"
# Function to log messages
function Log-Message {
param ([string]$msg)
$timestamp = Get-Date -Format "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"
Add-Content -Path $logFile -Value "$timestamp $msg"
}
# Main workflow
try {
Connect-VIServer -Server <vcenter-address> -User <username> -Password <password> -ErrorAction Stop
Log-Message "Connected to vCenter."
# Try to get VM info
$vms = Get-VM
Log-Message "Successfully retrieved VM inventory. Total: $($vms.Count)"
}
catch {
Log-Message "ERROR: $($_.Exception.Message)"
}
finally {
Disconnect-VIServer -Server * -Confirm:$false
Log-Message "Disconnected from vCenter."
}
3. Python Error Handling and Logging
Below is a Python wrapper to call the script and log errors or results from the PowerShell execution.
import subprocess
import datetimelogfile = r"C:Temppython_automation_log.txt"
def log_message(msg):
with open(logfile, "a") as f:
now = datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
f.write(f"{now} {msg}n")
ps_script = r"C:Tempvm_error_handling.ps1"
try:
completed_process = subprocess.run([
"powershell.exe",
"-ExecutionPolicy", "Bypass",
"-File", ps_script
], capture_output=True, text=True, timeout=120)
if completed_process.returncode == 0:
log_message("PowerShell script ran successfully.")
if completed_process.stdout:
log_message(f"Output: {completed_process.stdout}")
else:
log_message(f"ERROR: {completed_process.stderr}")
except Exception as e:
log_message(f"Python Exception: {str(e)}")
4. Integration with Aria for Logs (Optional)
For centralized log analysis, send script logs to Aria for Logs.
This is typically accomplished by:
- Sending logs via syslog from your automation server to Aria for Logs.
- Using a PowerShell or Python module to forward specific events.
You can configure Windows Event Logs or custom log forwarding.
See VMware docs: Aria for Logs Documentation
5. Diagram: Logging Workflow
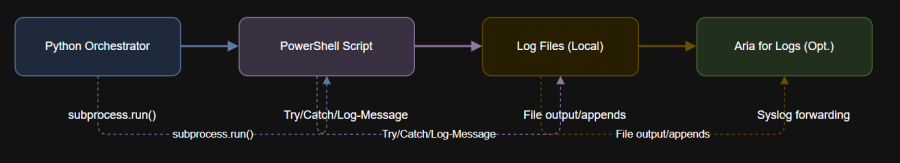
6. Troubleshooting Tips
- Check that your script log file paths exist and are writable.
- For errors not being logged, confirm all actions are inside try/catch blocks.
- To see real-time logs, use
Get-Content -Path C:Tempautomation_log.txt -Waitin PowerShell.
7. Further Reading
8. Conclusion and Next Steps
You have learned how to add robust error handling and logging to both PowerCLI and Python scripts, and how to centralize logs with Aria for Logs.
This ensures your VMware automation is safer, more auditable, and easier to troubleshoot.
Next up: In Article 7, you will learn about scheduling scripts and automation best practices for production VMware environments.






